A Colonial Blueprint: The Remaking of Moindou
In the administrative area known as Moindou in New Caledonia, there previously existed two indigenous Kanak tribes: Little Moindou and Great Moindou. Following an attack by these tribes on the Moindou agricultural center on 21 July 1878, the area was completely destroyed on 22 July 1878 as a result of punitive measures carried out by French colonial forces. This event is regarded as part of the broader wave of local resistance and uprisings that occurred in New Caledonia during that period and reflects the Kanak communities’ struggle against colonial occupation.
Archival documents dating from 1886 indicate that, due to its favorable geographical position, the Moindou administrative district was subsequently designated as a principal settlement by the French colonial authorities. Between 1880 and 1886, France initiated the rapid construction and development of the village, which was noted as the only settlement in New Caledonia to have been built at such a rapid pace during that time.
Several roads were constructed around the village—Moindou–Téari, Moindou–La Foa, Moindou–Tango, Moindou–Koné, and Moindou–Bourail. The development of this infrastructure relied primarily on the labor of prisoners held in penal colonies, who played a crucial role in its construction. These processes were carried out under strict supervision by the colonial authorities.
The restoration and development of this area were also driven by a policy of settler migration. Migrant families transferred from France and Germany were resettled in the region. In this respect, Moindou represents a typical example of both the colonial forced-labor system and European settler colonization policies.
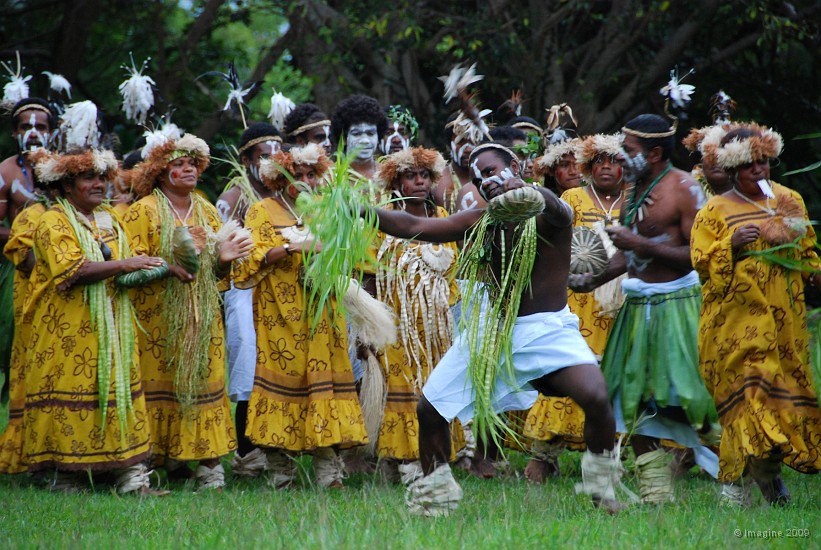

The Pilou-Pilou: A Banned Dance of Memory and Resistance
Since 1853, when this island archipelago became a French colony, a systematic policy of assimilation was pursued against the culture of the indigenous Kanak people. As a result of...
Read more
Penal Colonies: The Forced Labor Foundations of New Caledonia
From the mid-nineteenth century onward, New Caledonia became for France not merely a remote island in the Pacific, but one of the central pillars of its imperial penal policy. Following the official a...
Read more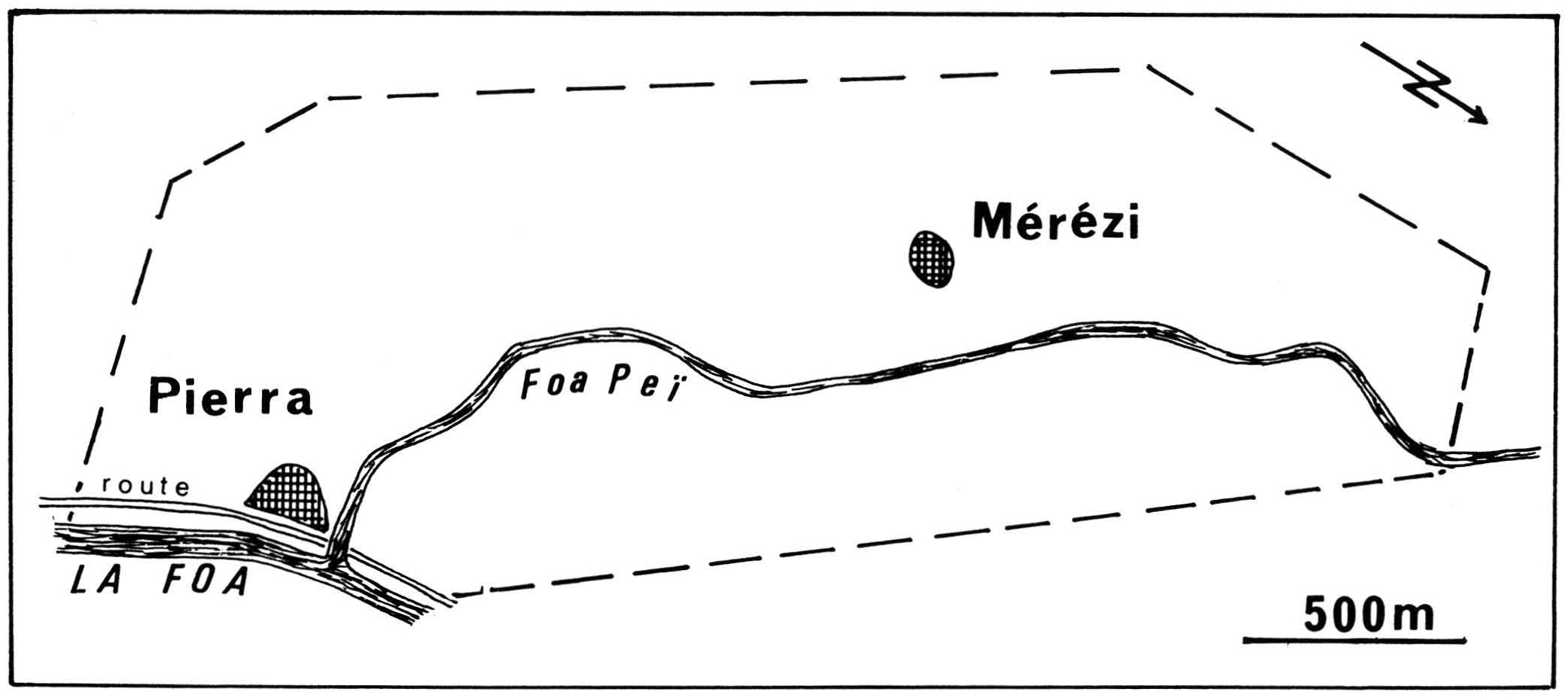
1877: The Abolition of a Reserve and the Theft of Kanak Land
The land exploitation affecting the villages of Pierra and Mérézi constitutes a clear example of France’s colonial policy of land confiscation and dispossession in New Caledonia. This policy involved...
Read more
Colonial Gold: The Montagne d’Or Project and Lasting Exploitation in French Guiana
Group (AMG) is one of the leading French companies operating in the gold-mining sector in French Guiana. Sources such as the French Geological Survey (BRGM) and the journal Mining provide statistical...
Read more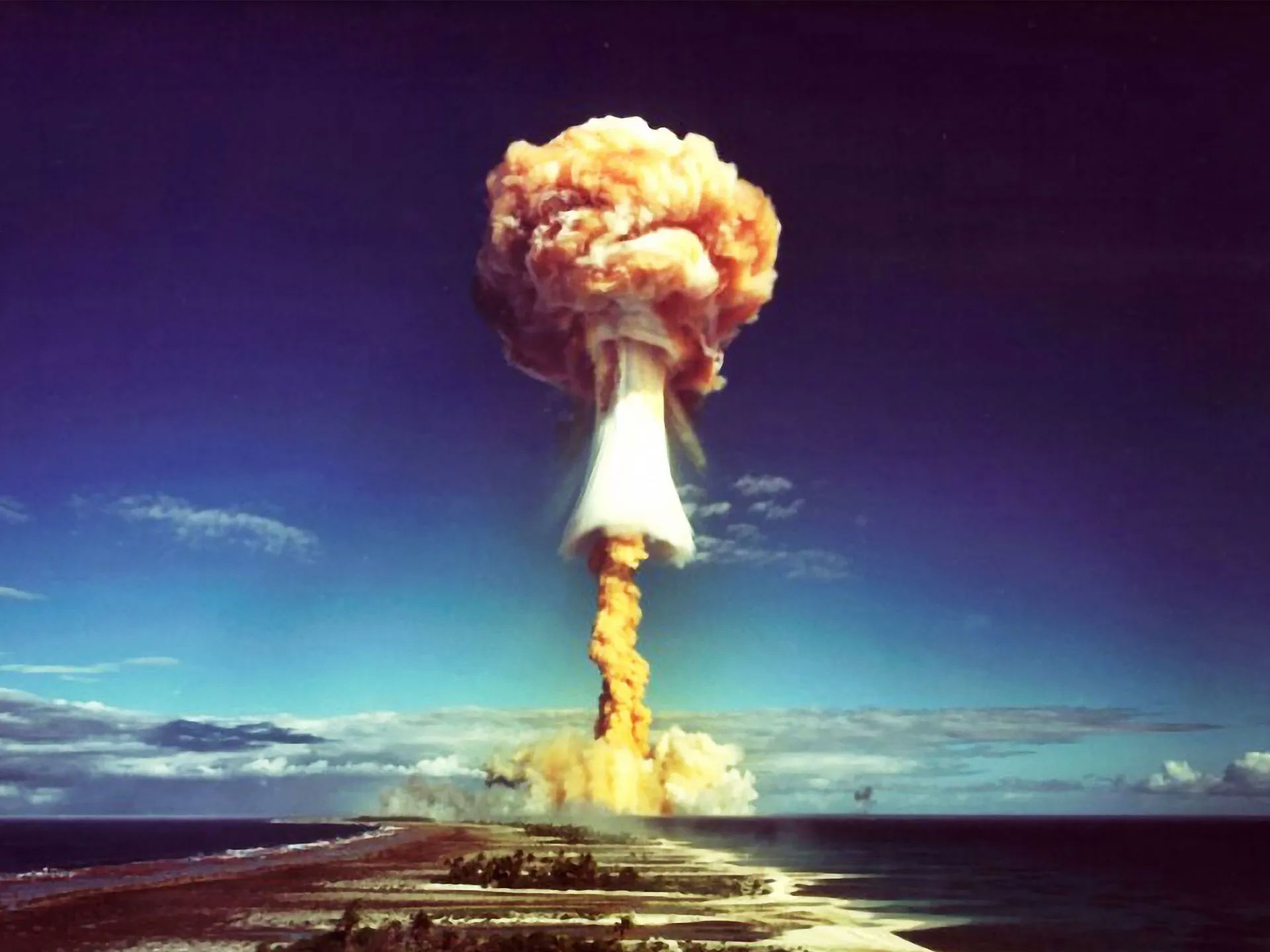
Tests, Lies, and Legacy: Radioactive Colonialism in French Polynesia
French Polynesia, a tropical archipelago located in the South Pacific, is known not only for its natural beauty and cultural richness, but also for having been the site of some of the darkest nuclear...
Read more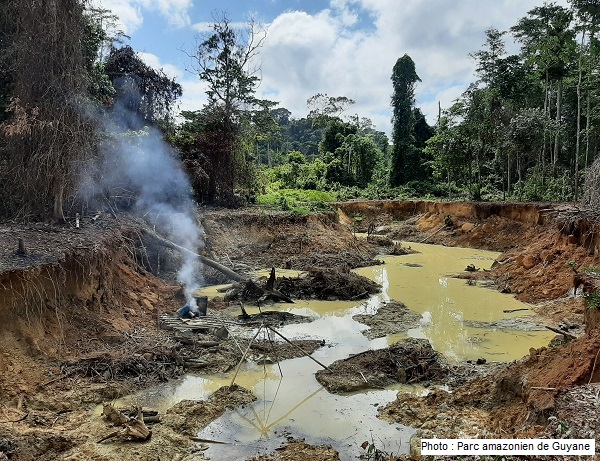
Colonial Contamination: Gold Mining and Environmental Degradation in French Guiana
In French Guiana, gold mining is particularly widespread. The mining process involves the use of heavy metals such as mercury, which leads to the contamination of water bodies and soil. As mercury is...
Read more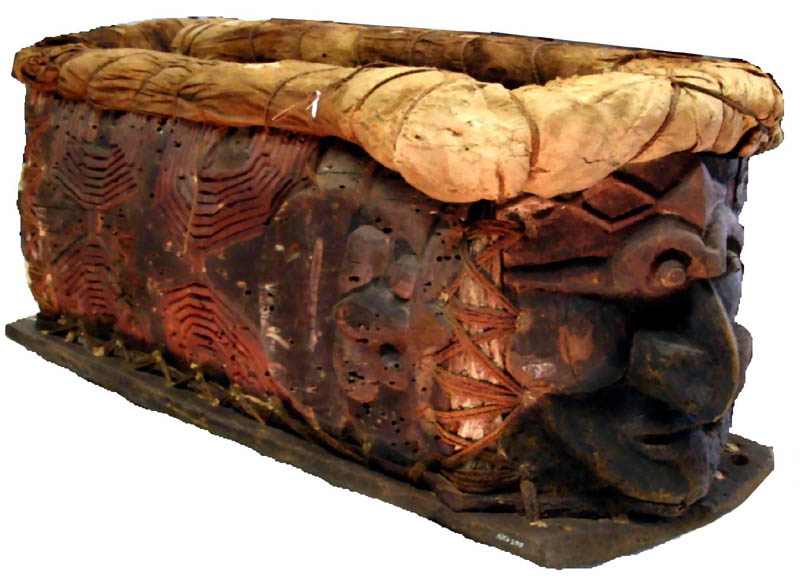
Kanak Ossuary: A Funerary Artifact of Architectural Reuse
The term “ossuaire” refers to places or containers used for the storage of human bones, particularly where skeletal remains are gathered and preserved. Ossuaries are typically found in ...
Read more
The Saponé Headdress: From Enthronement Ritual to Protected Heritage
The “Saponé” headdress is a traditional accessory made from woven straw and decorated with leather. It takes its name from the village of Sapone, where it is primarily produced. Sapone is located appr...
Read more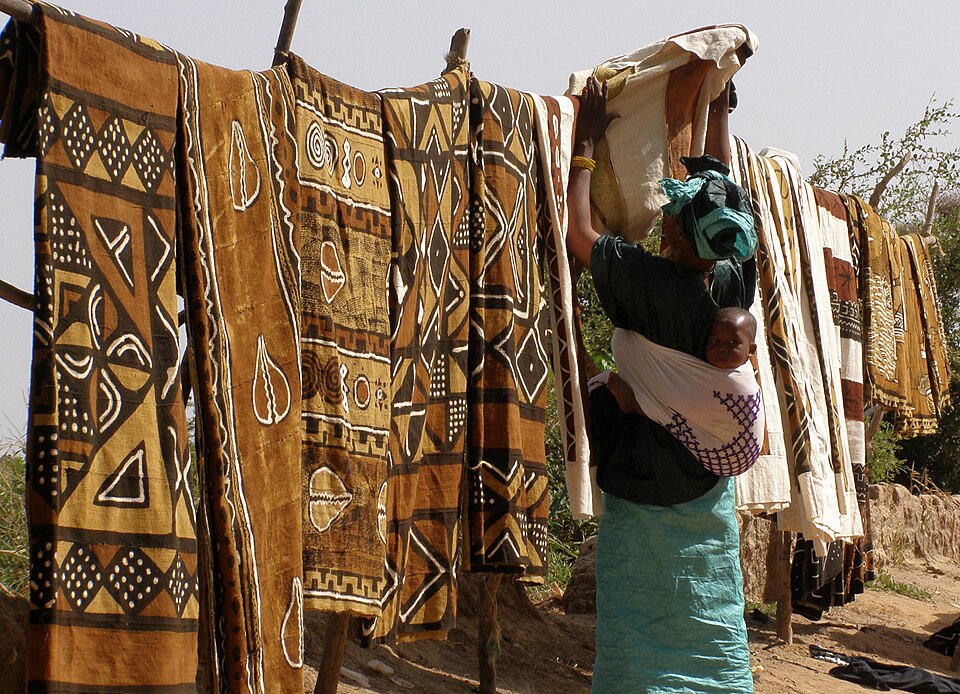
Bogolan: A Malian Textile Woven with Earth and Symbolism
“Bogolan” – African Textile Art (Mali)The term “Bogolan” literally means “made with earth” in the Bambara language. This centuries-old technique originated in Mali. Although it has also been adopted i...
Read more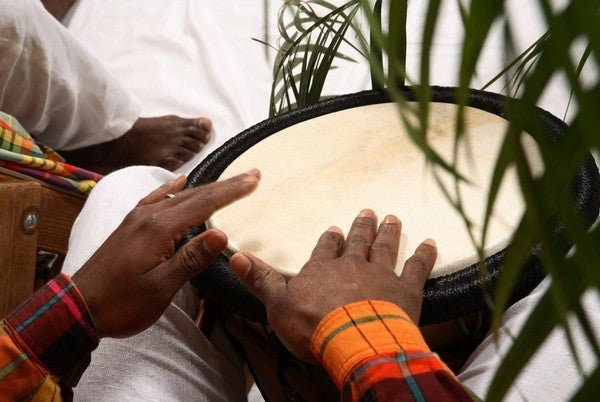
Gwoka: The Seven Rhythms of Memory and Resistance
Gwoka music is a musical genre performed on percussion instruments by people of African descent living in Guadeloupe. Gwoka emerged during the period of slavery and is composed of ...
Read more
From Forbidden Fabrics to Forced Assimilation: Colonial Dress Code
French Guiana, as a region with a rich and diverse ethnic composition, has for centuries been home to a wide range of Indigenous and African-descended peoples who developed distinctive cultural expres...
Read more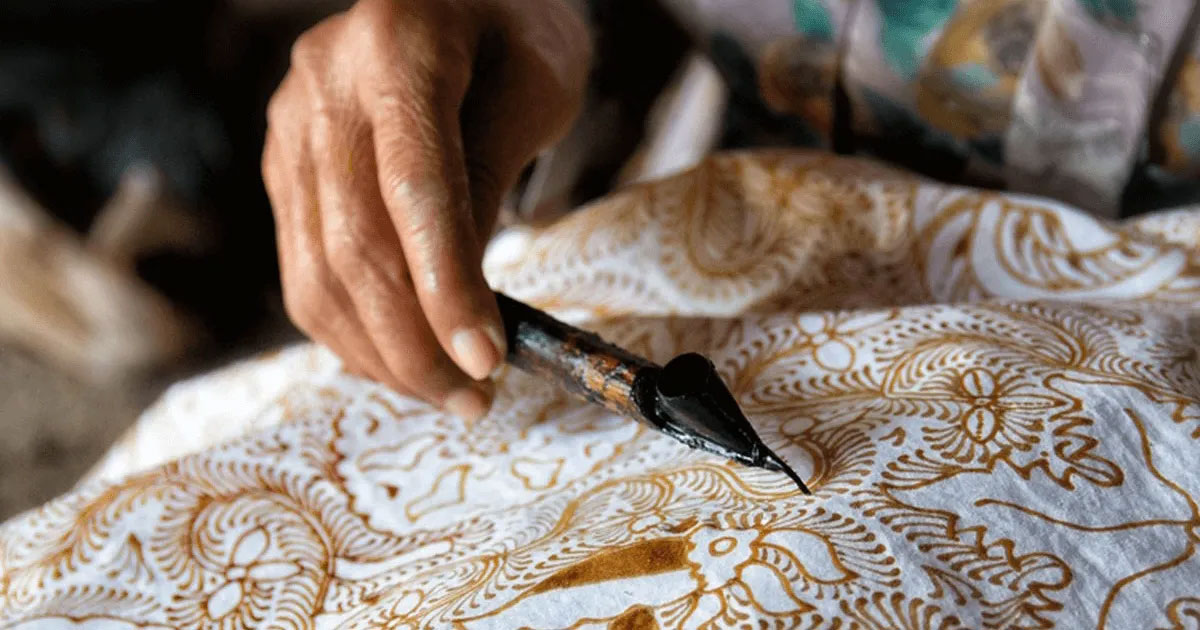
Salouva and Batik: Dismantling a Heritage Through Clothing
The peoples living on this island have, for centuries, possessed distinct cultural traditions and customs, with traditional clothing forming an inseparable part of their identity. However, a...
Read more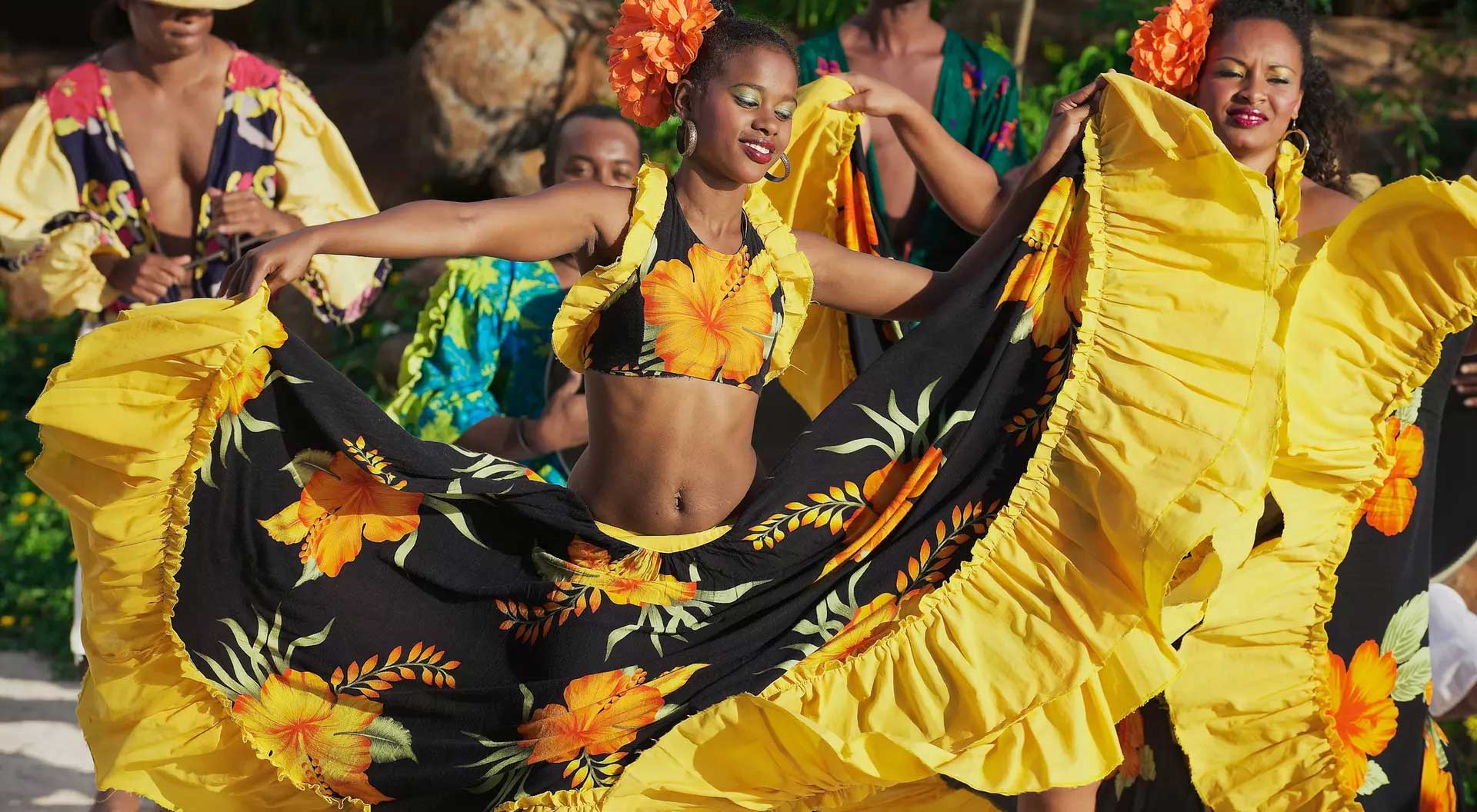
From Slave Resistance to Creole Identity: Réunion's Cultural Tapestry
The national cultural heritage of Réunion Island encompasses a rich legacy shaped by the interweaving of African, Indian, Malagasy, and European cultures. Traditional decorative objects include basket...
Read more
The Dimitile Maroons Museum: A Memorial to Freedom in the Mountains
The Dimitile Maroons Museum (Musée du Marronnage de Dimitile), located on Réunion Island, is both a site of historical memory and a symbolic space of anti-colonial resistance. The museum is situated i...
Read more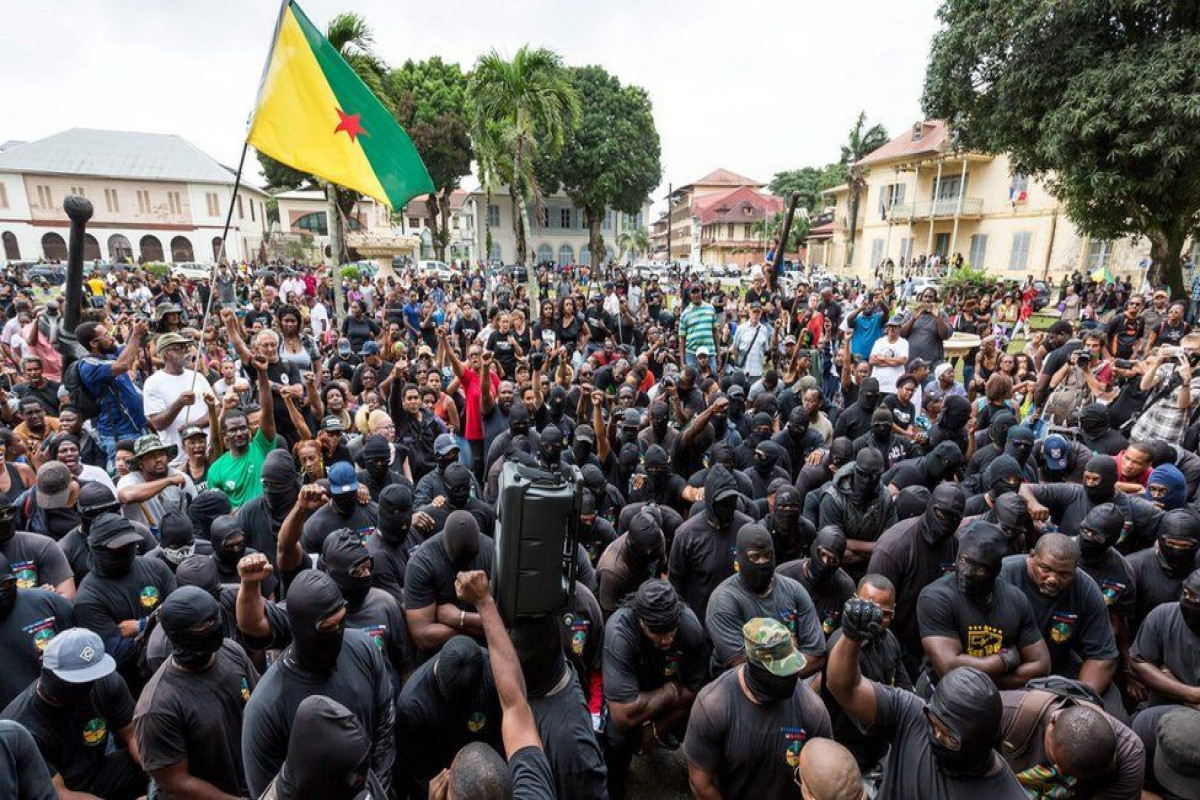
The 2017 General Strike: Guiana's Awakening Against Colonial Neglect
The “Pou Lagwiyann Dékolé” movement (“Let Guiana Take Off”) was a large-scale popular uprising that emerged in March–April 2017 in French Guiana, in response to deep-rooted social,...
Read more